[7] EasyCalib: Simple and Low-Cost In-Situ Calibration for Force Reconstruction with Vision-Based Tactile Sensors [Publication] [Preprint_PDF] [EasyCalib]
- Mingxuan. Li, Lunwei. Zhang, Yen. Hang. Zhou, Tiemin. Li, and Yao. Jiang
- Published in IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, Jul. 2024.
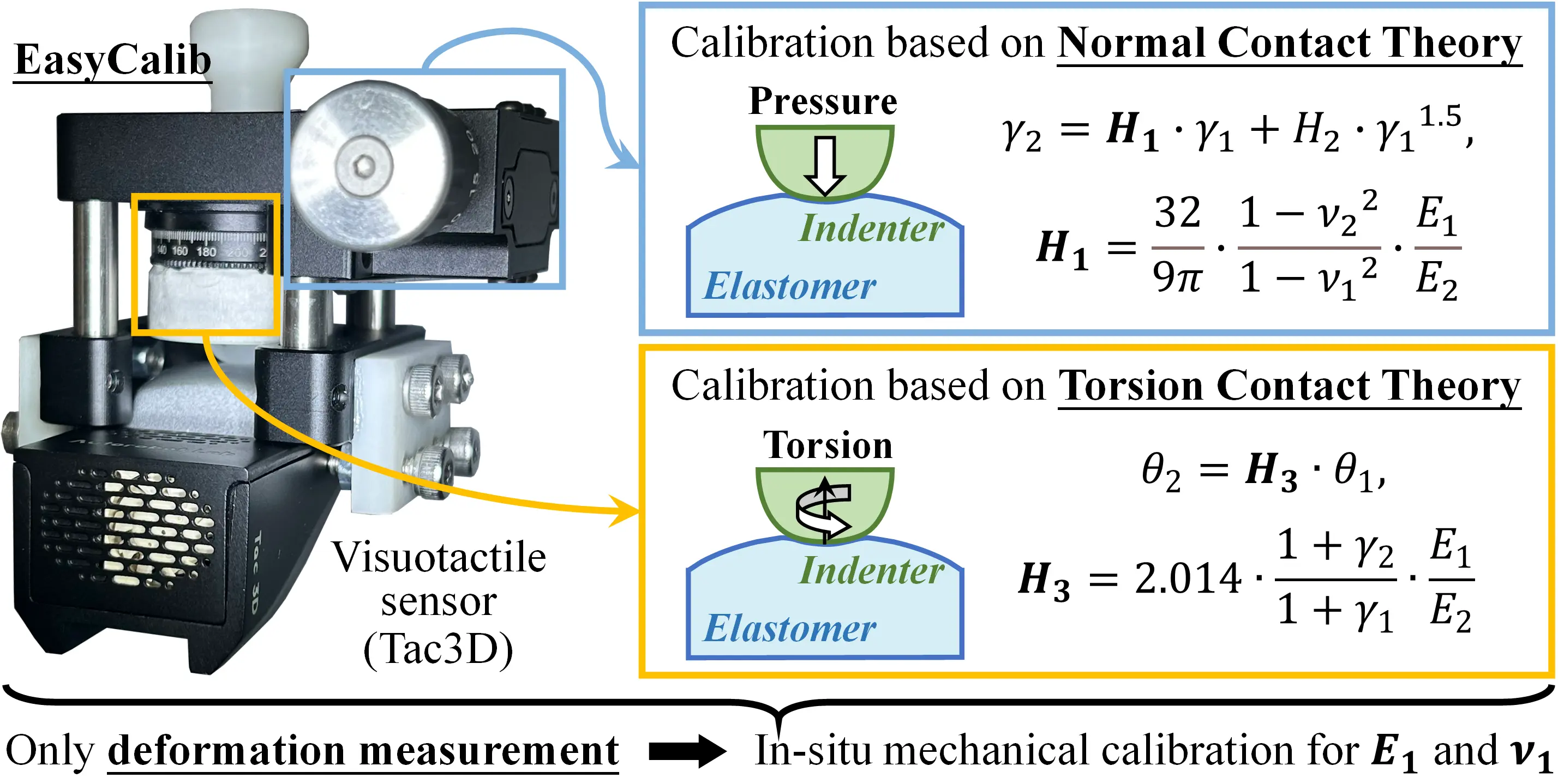
- This article describes an in-situ calibration device, EasyCalib, for routinely measuring mechanical parameters (Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio) of visuotactile sensors. Detailed derivations of theories ensure that it is low-cost, user-friendly, and does not require F/T sensors.
[6] OneTip Is Enough: A Non-Rigid Input Device for Single-Fingertip Human-Computer Interaction With 6-DOF [TechRxiv] [Preprint_PDF] [Video]
- Mingxuan. Li, Yen. Hang. Zhou, Lunwei. Zhang, Tiemin. Li, and Yao. Jiang
- Preprint in TechRXiv, submitted to Sensors and Actuators: A. Physical, Feb. 2024.
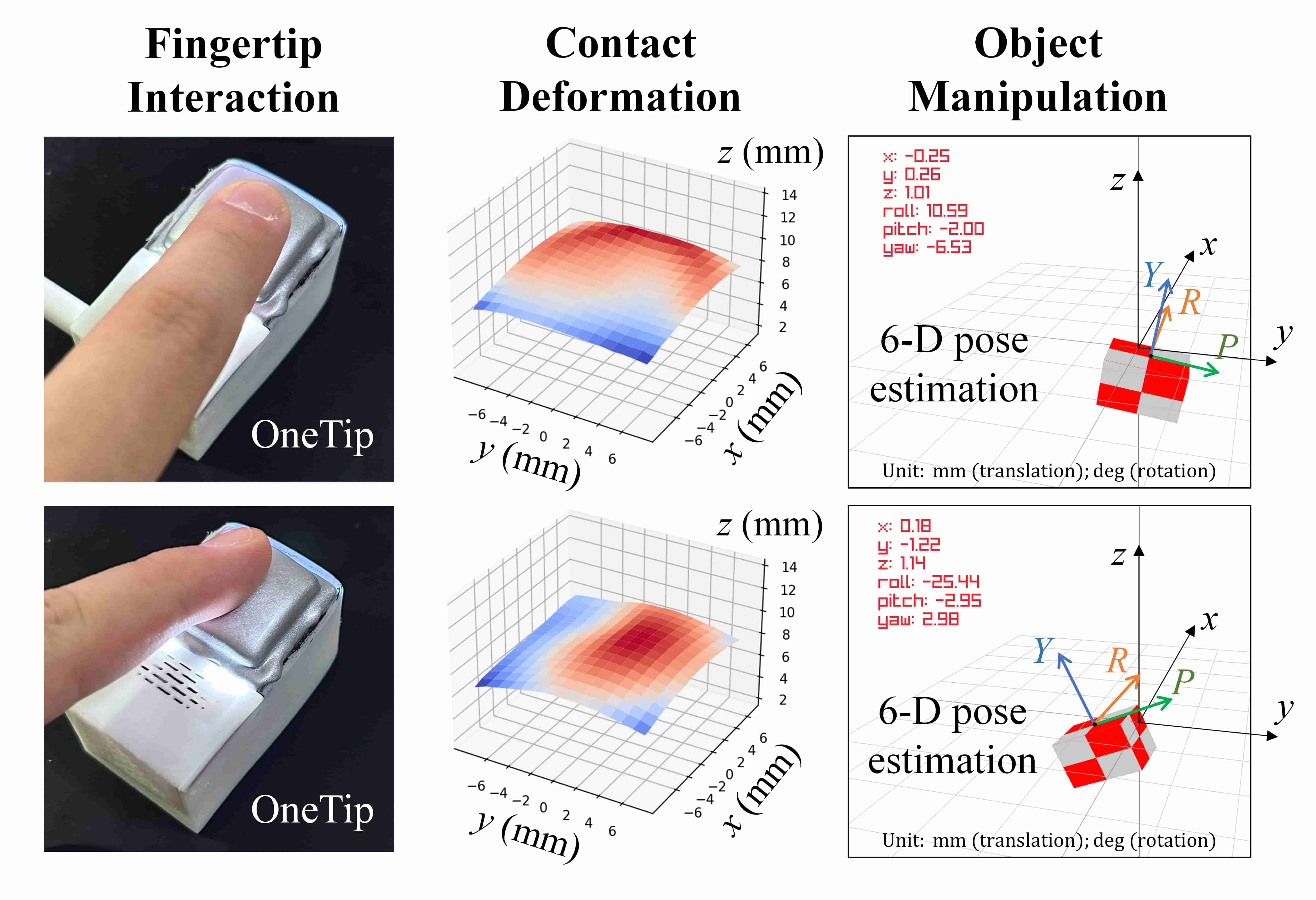
- This article introduces visuotactile sensing technology into the field of human-computer interaction. We present a novel HCI device, OneTip, which can achieve 6-DOF input with just one fingertip. Evaluations and application explorations were conducted to explore the performance and usability of OneTip.
[5] Incipient Slip-Based Rotation Measurement via Visuotactile Sensing During In-Hand Object Pivoting [arXiv] [Preprint_PDF] [Video] [Poster] [Slides]
- Mingxuan. Li, Yen. Hang. Zhou, Tiemin. Li, and Yao. Jiang
- Preprint in arXiv, accepted by 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Jan. 2024.
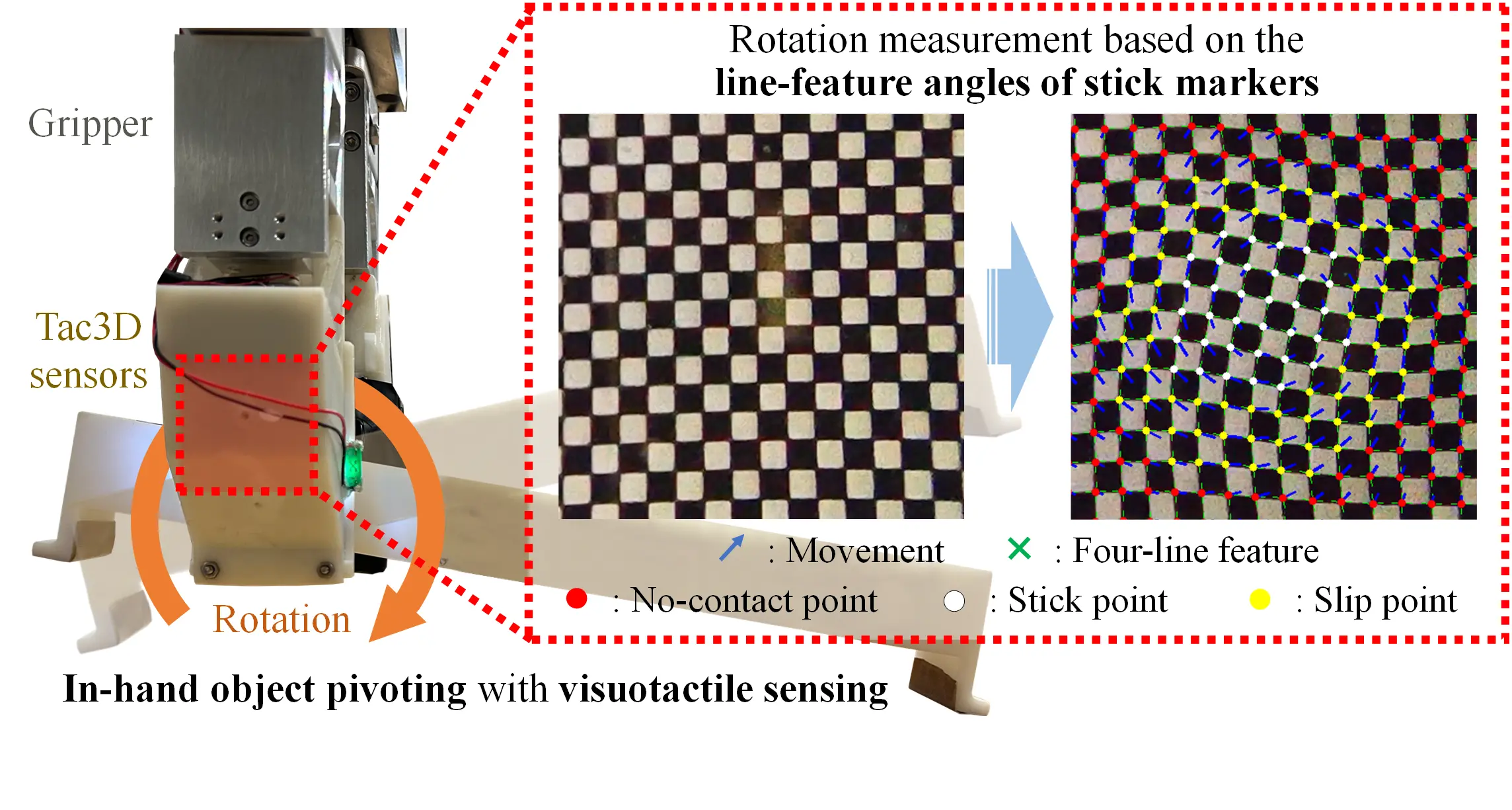
- This paper describes a generalized 2-d contact model under pivoting, and proposes a measurement method of rotation angle based on the line features in the stick region. It could achieve the average measurement errors of 0.17°±0.15° (static) and 1.34°±0.48° (dynamic).
[4] Real-time and Robust Feature Detection of Continuous Marker Pattern for Dense 3-D Deformation Measurement [Publication] [Preprint_PDF]
- Mingxuan. Li, Yen. Hang. Zhou, Tiemin. Li, and Yao. Jiang
- Published in Measurement, Nov. 2023.
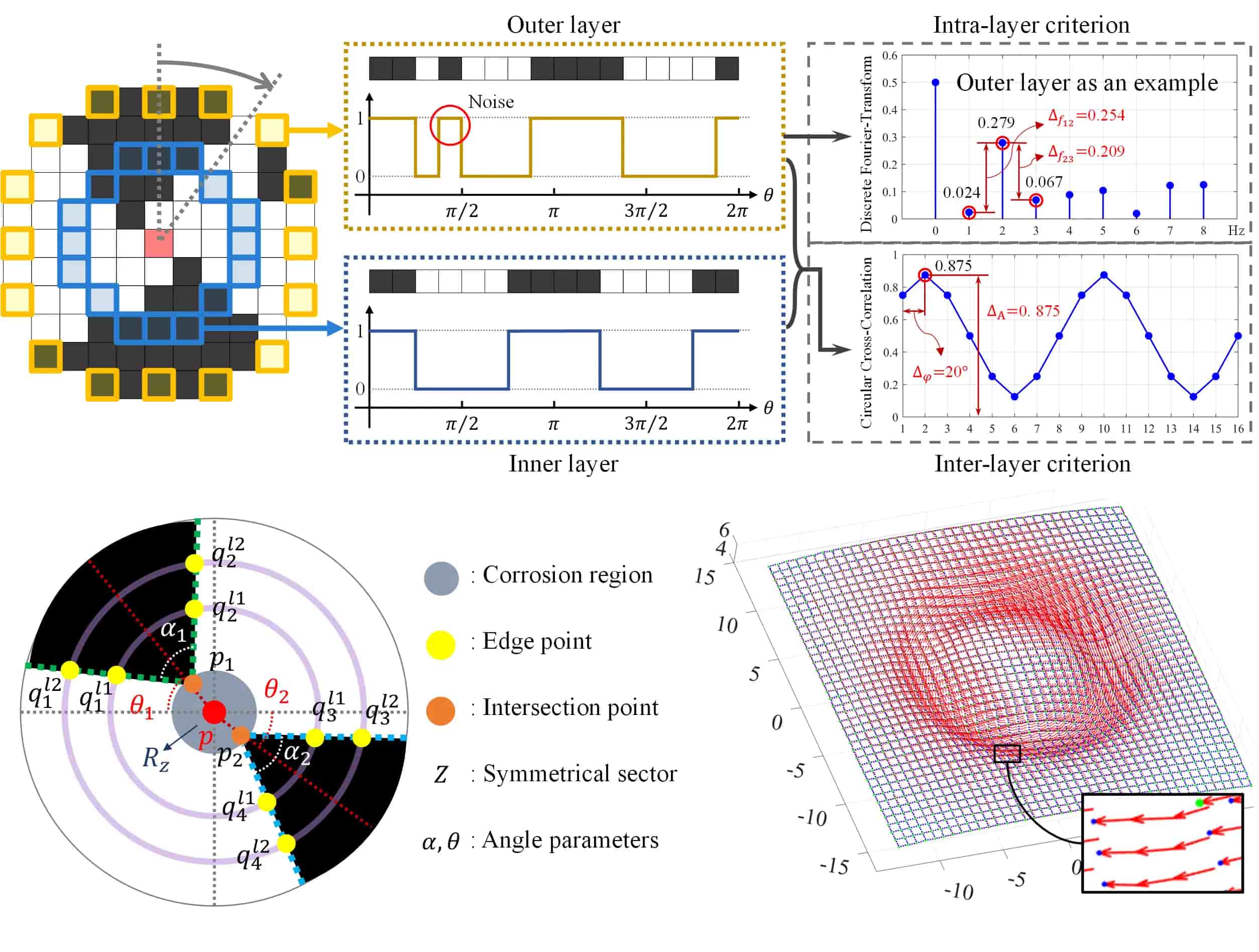
- This article achieves the measurement of dense 3-d contact deformation (10.7 markers per square millimeter). We propose a feature detection method applicable to visuotactile sensors based on continuous marker patterns (CMP), which reflects a clear superiority in real-time and reliability performance.
[3] Improving the Representation and Extraction of Contact Information in Vision-based Tactile Sensors Using Continuous Marker Pattern [Publication] [Preprint_PDF]
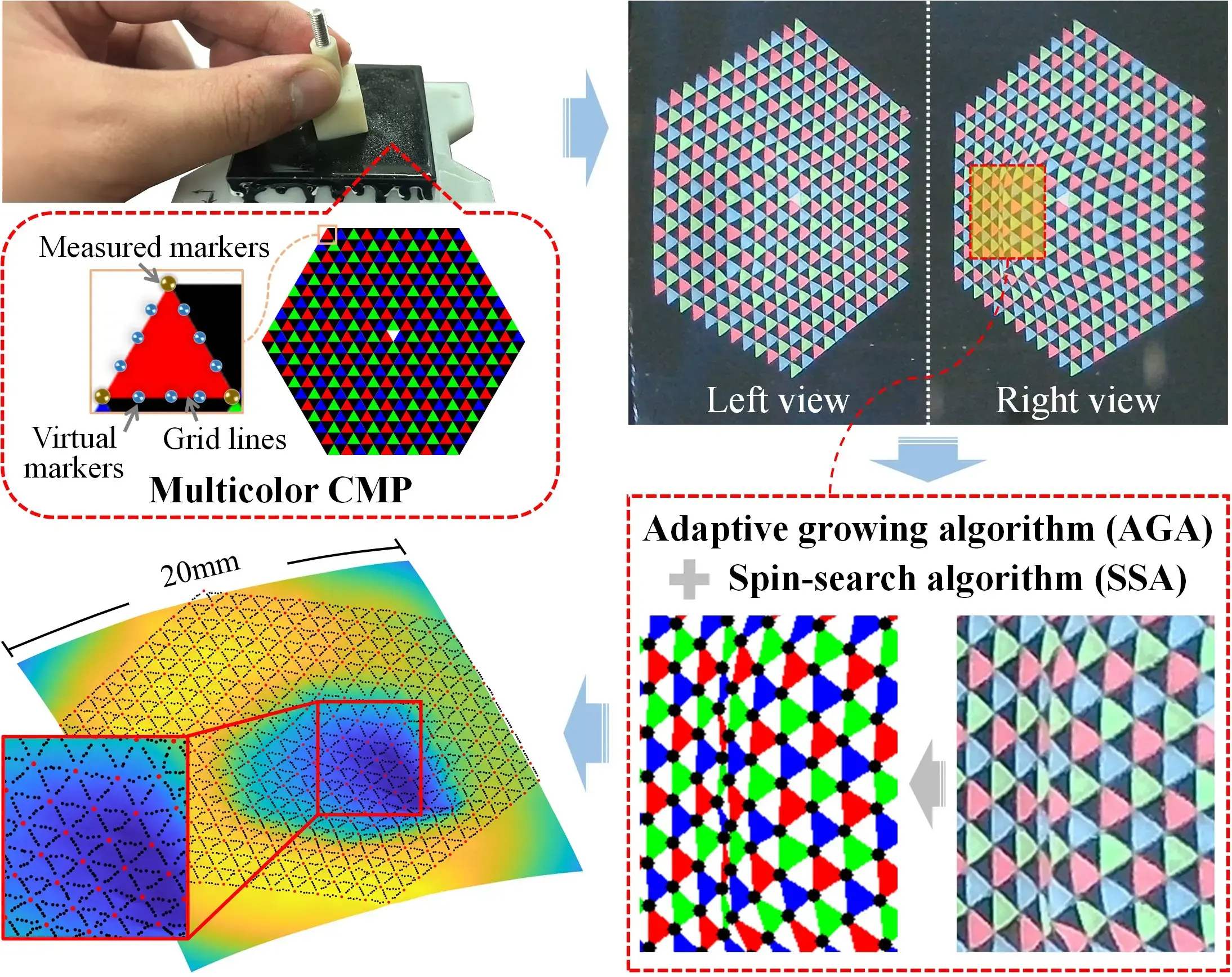
- Mingxuan. Li, Yen. Hang. Zhou, Tiemin. Li, and Yao. Jiang
- Published in IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, Sep. 2023.
- This article highlights the importance of raw representation and extraction in visuotactile perception. We propose a new multicolor CMP method (including pattern design, algorithm optimization, and preparation process) for enhancing the performance of vision-based tactile sensors.
[2] Marker Displacement Method Used in Vision-Based Tactile Sensors—From 2-D to 3-D: A Review [Publication] [Preprint_PDF]
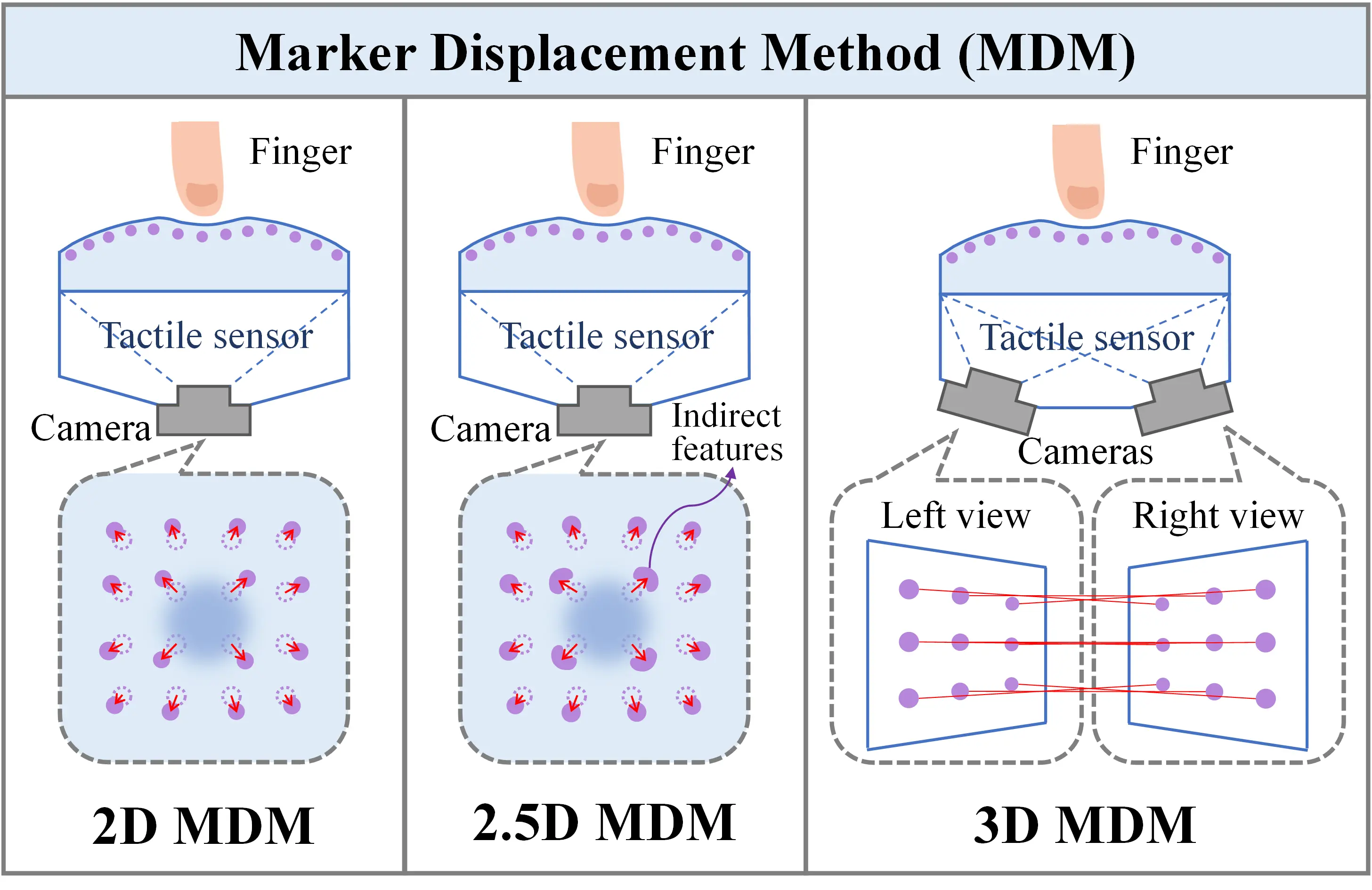
- Mingxuan. Li, Tiemin. Li, and Yao. Jiang
- Published in IEEE Sensors Journal, Apr. 2023.
- This article presents a detailed review and categorizing of the marker displacement method (MDM) used in vision-based tactile sensors. We classify MDM into three typical categories based on the dimensionality perspective for the first time: 2D MDM, 2.5D MDM, and 3D MDM.
[1] Continuous Marker Patterns for Representing Contact Information in Vision-Based Tactile Sensor: Principle, Algorithm, and Verification [Publication] [Preprint_PDF]
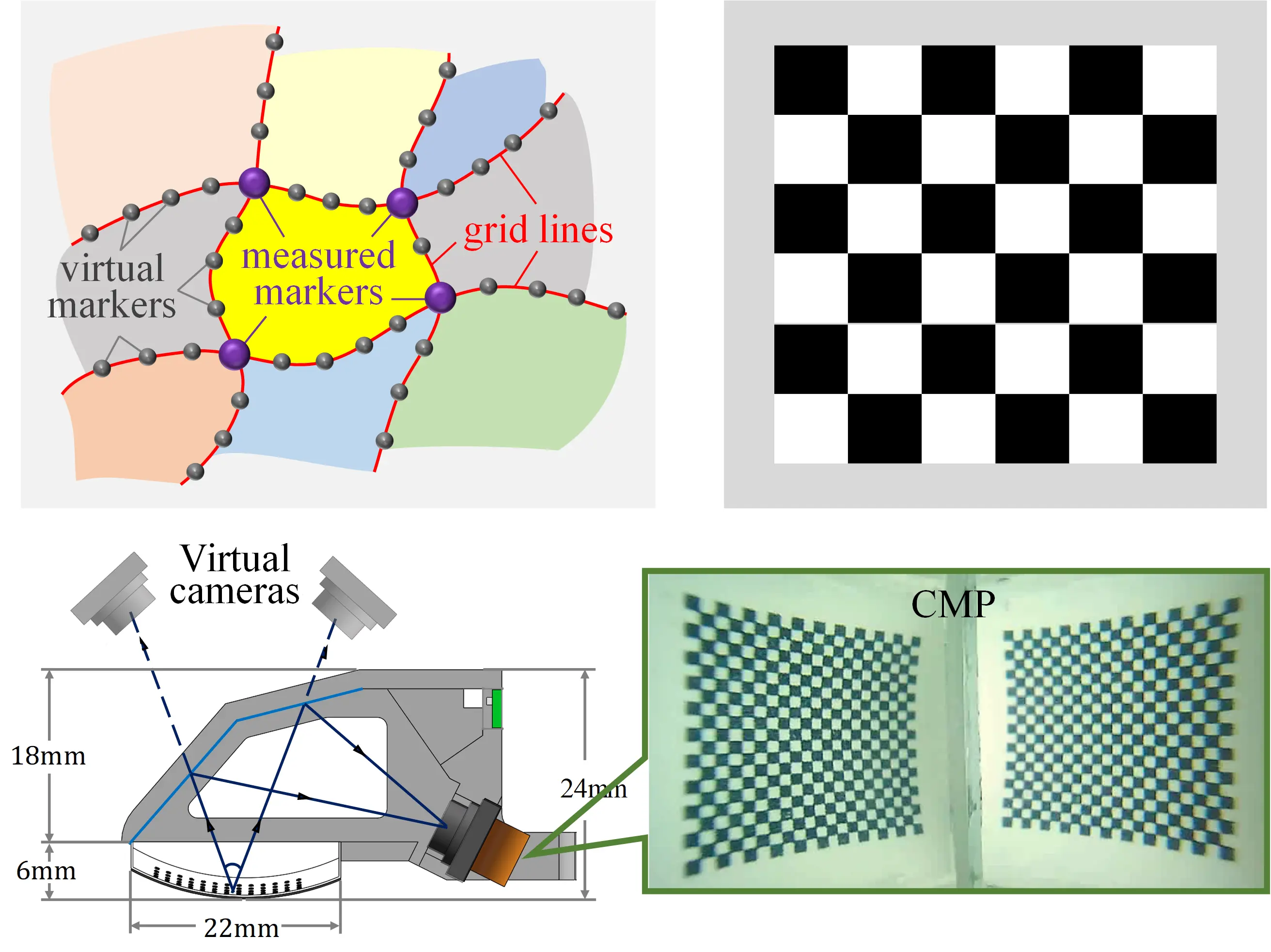
- Mingxuan. Li, Lunwei. Zhang, Tiemin. Li, and Yao. Jiang
- Published in IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, Aug. 2022.
- This article innovatively proposes the idea of the continuous marker pattern (CMP) and three basic design principles to optimize tactile representation and extraction in visuotactile sensors. Simulation and prototype experiments prove the tactile sensors with CMP outperformed the distributed marker pattern (DMP) regarding measurement precision, resolution, and reliability.